The flame test lab is a cornerstone in chemistry education, enabling students to identify metal ions through distinctive flame colors. It’s a fundamental, visually captivating technique that introduces students to elemental analysis, with numerous resources like flame test lab answers PDF available for guidance and understanding.
1.1. What is a Flame Test?
A flame test is a laboratory procedure used to identify the presence of specific metal ions in a compound. By heating a sample in a flame, the emitted light is analyzed for characteristic colors, which correspond to specific elements. This method relies on the emission spectra of metals, providing a visual and qualitative way to detect metallic elements. It is a simple yet effective technique commonly used in chemistry labs to determine the composition of unknown substances.
1.2. Importance of Flame Tests in Chemistry
Flame tests are a fundamental technique in chemistry, providing a rapid and qualitative method to identify metal ions in compounds. By observing the characteristic colors emitted during combustion, chemists can determine the presence of specific elements. This method is not only educational but also practical, aiding in elemental analysis and quality control. Flame tests are widely used in labs and industries, making them a cornerstone of both academic and applied chemistry, with resources like flame test lab answers PDF offering detailed guidance.
1.3. Purpose of the Flame Test Lab
The flame test lab is designed to help students identify metal ions in compounds by observing the characteristic colors produced when these ions are heated in a flame. This hands-on experiment allows learners to distinguish between different elements based on their unique flame colors. By conducting this lab, students develop analytical skills, understand the relationship between elements and their properties, and gain practical experience in scientific observation and data interpretation, supported by resources like flame test lab answers PDF;

Materials and Equipment Needed
The flame test lab requires metal salt solutions, Bunsen burners, clean nichrome or platinum wire, flame-resistant mats, goggles, gloves, and lab coats. Refer to the flame test lab answers PDF for detailed lists and setup instructions.
2.1. List of Chemicals and Compounds
The flame test lab involves various metal salts dissolved in water, such as sodium chloride (NaCl), copper sulfate (CuSO₄), calcium chloride (CaCl₂), potassium chloride (KCl), and lithium chloride (LiCl). These compounds are chosen for their distinct flame colors. Additionally, metal wires like nichrome or platinum are used for heating the samples. Ensure all chemicals are in their purest form to avoid contamination. Refer to the flame test lab answers PDF for a comprehensive list of required compounds and their preparation methods.
2.2. Laboratory Equipment Required
The flame test lab requires a Bunsen burner, metal loops or nichrome wires for heating samples, and glass rods for holding solutions. Heat-resistant mats and lab tongs are essential for safe handling. A blue or yellow flame is preferred to avoid color interference. Goggles and lab coats are mandatory for safety. Ensure all equipment is clean and in good condition. Detailed setup instructions can be found in the flame test lab answers PDF for optimal experiment execution.
2.3. Safety Gear and Precautions
Essential safety gear includes goggles, lab coats, and heat-resistant gloves to protect against chemical splashes and heat. Tie back long hair and avoid loose clothing. Ensure the workspace is clear of flammable materials. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby. Handle equipment carefully to prevent burns. Wash hands thoroughly after handling chemicals. In case of eye contact with chemicals, flush with water for at least 15 minutes. Properly dispose of waste materials. Refer to the flame test lab answers PDF for detailed safety protocols.
Step-by-Step Procedure
Prepare solutions, conduct flame tests, observe colors, and record results. Refer to the flame test lab answers PDF for detailed procedural guidance and accuracy.
3.1. Preparing the Solutions
To prepare the solutions, dissolve metallic salts in distilled water using safety gear. Ensure each salt is fully dissolved to avoid contamination. Handle chemicals cautiously, wearing gloves and goggles. Use clean glassware to prevent cross-contamination. For accurate results, follow the instructions in the flame test lab answers PDF. Label each solution clearly for identification during testing. This step is crucial for reliable flame test outcomes.
3.2. Conducting the Flame Test
Dip a clean Nichrome wire into the solution, holding it in the flame of a Bunsen burner. First, heat the wire to red-hot to remove contaminants. Let it cool slightly, then repeat with the sample. Observe the flame color carefully, noting its intensity and hue. If the color is faint, repeat the process. Document your observations for later analysis. Always handle the wire with tongs and ensure the burner is at a safe setting. Refer to the flame test lab answers PDF for guidance.
3.3. Observing and Recording Results
Carefully observe the flame color produced and record it in a data table. Note the intensity and any patterns. Use a flame test lab answers PDF as a reference to match observed colors with known metals. Ensure all observations are accurate and reproducible. Minimize distractions and focus on the flame’s appearance. Document the chemical used, flame color, and corresponding metal ion. This step is crucial for drawing reliable conclusions and verifying the accuracy of your experiment.
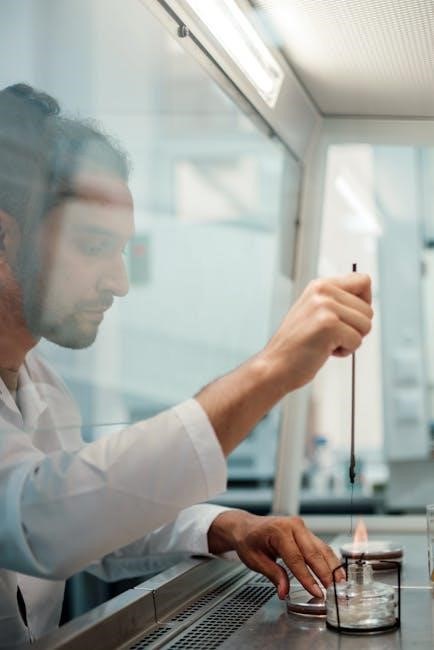

Understanding Flame Test Results
Understanding flame test results involves interpreting the characteristic flame colors to identify specific metals. This process is essential for chemical analysis and education, often guided by flame test lab answers PDF.
4.1. Characteristic Flame Colors of Metals
Characteristic flame colors of metals are unique and help in identifying specific elements. Sodium produces a bright yellow flame, while copper emits a blue color. Calcium burns with an orange-red hue. These distinct colors are due to electron transitions in the metal ions, emitting specific wavelengths. By comparing observed colors to known data, students can accurately identify metals. Resources like flame test lab answers PDF provide reference charts for these colors, aiding in precise identification and analysis.
4.2. Interpreting the Data
Interpreting flame test data involves matching observed flame colors to known metal ions. By comparing results with reference charts, students can identify the elements present. Accurate observations and careful recording are crucial for reliable conclusions. If results are inconsistent, retesting or consulting resources like flame test lab answers PDF can help validate findings. This step reinforces understanding of how atomic structure influences flame color, ensuring precise and meaningful interpretations of experimental data.

Common Metals and Their Flame Colors
Metals like sodium, copper, and calcium produce distinct flame colors. Sodium yields a bright yellow flame, while copper burns blue, and calcium emits an orange-red hue.
5.1. Sodium (Na) ⎼ Bright Yellow Flame
Sodium produces a striking bright yellow flame when subjected to a flame test. This distinctive coloration is due to the excitation of sodium atoms, which emit light at a specific wavelength. The intense yellow hue is easily recognizable and serves as a reliable indicator of sodium’s presence. In educational settings, this vivid reaction is often used to demonstrate flame test principles, making sodium a common element in such experiments. Resources like flame test lab answers PDF often highlight this characteristic for easy identification.
5.2. Copper (Cu) ⎻ Blue Flame
Copper produces a distinctive blue flame when subjected to a flame test. This color arises from the energy released as copper atoms return to their ground state after excitation. The blue hue is less vivid than sodium’s yellow but still easily identifiable. Copper’s flame test is often used in educational labs to teach students about metal ion identification. Resources such as flame test lab answers PDF provide detailed insights and visuals to aid in recognizing this characteristic blue coloration.
5.3. Calcium (Ca) ⎼ Orange-Red Flame
Calcium produces a vibrant orange-red flame during a flame test, a result of its unique atomic structure. This intense color is easily distinguishable and often used in educational labs to demonstrate metal ion identification. Resources like flame test lab answers PDF provide detailed descriptions and images to help students recognize and differentiate calcium’s flame from others, such as sodium’s yellow or copper’s blue, enhancing learning and experimentation in chemistry.

Safety Tips and Best Practices
Always wear goggles and gloves to protect against chemical splashes and heat exposure. Ensure the lab area is clear of flammable materials.
Use tongs to handle hot equipment and keep a fire extinguisher nearby. Never leave flames unattended and follow proper chemical handling procedures.
6.1. Handling Chemicals Safely
When handling chemicals in a flame test lab, always wear protective goggles and gloves to prevent exposure. Ensure all substances are stored in properly labeled containers and kept away from heat sources. In case of skin contact, wash thoroughly with water. If chemicals come into contact with eyes, flush immediately with water for 15 minutes. Dispose of waste according to lab guidelines to maintain a safe environment. Refer to the flame test lab answers PDF for detailed safety protocols.
6.2. Proper Use of Lab Equipment
Always handle lab equipment with care to ensure safety and accuracy. Use tongs or a nichrome wire to hold samples in the flame, avoiding direct contact with gloves. Adjust the Bunsen burner to achieve a clear, blue flame for consistent results. Keep the work area clean and well-ventilated. Regularly inspect equipment for damage and follow manufacturer guidelines. Proper use of lab equipment is crucial for obtaining reliable flame test results. Consult the flame test lab answers PDF for detailed equipment handling instructions.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Faint flame colors may indicate low concentration or improper heating.
- Contamination can skew results; ensure samples are pure.
- Consult the flame test lab answers PDF for detailed solutions to common problems.
7.1. Faint or Unusual Flame Colors
Faint or unusual flame colors can occur due to low metal ion concentration or improper heating. Ensure solutions are pure and sufficiently heated. Contamination may also cause atypical results. Refer to the flame test lab answers PDF for troubleshooting guides and solutions.
7.2. Contamination of Samples
Contamination of samples can lead to inaccurate flame test results. Improper handling, unclean equipment, or cross-contamination from other substances may cause this issue. To prevent contamination, ensure all equipment is thoroughly cleaned and dried before use. Use pure chemical solutions and handle them with care. Refer to the flame test lab answers PDF for detailed guidance on maintaining sample integrity and avoiding contamination during the experiment.
The flame test lab offers valuable insights into identifying metal ions. For further learning, consult the flame test lab answers PDF, providing detailed results and explanations.
8.1. Summary of the Lab Experience
The flame test lab provides hands-on experience in identifying metal ions through characteristic flame colors. Students observe and record distinct hues, enhancing their understanding of elemental analysis. The lab reinforces chemical principles and practical skills, such as safely handling equipment and interpreting results. It also highlights the importance of precise observations in scientific investigations. Additional resources, including flame test lab answers PDF, offer further guidance and support for mastering this fundamental technique.
8.2; Where to Find Flame Test Lab Answers PDF
Flame test lab answers in PDF format are widely available online for educational purposes. Websites like FlameTestLabAnswersKey and educational platforms offer free downloads. Additionally, resources from Flinn Scientific and Quizlet provide comprehensive guides. Students can also find detailed lab manuals and answer keys through academic databases or by searching specific keywords on search engines like Google. Ensure to use reputable sources for accurate and reliable information.




