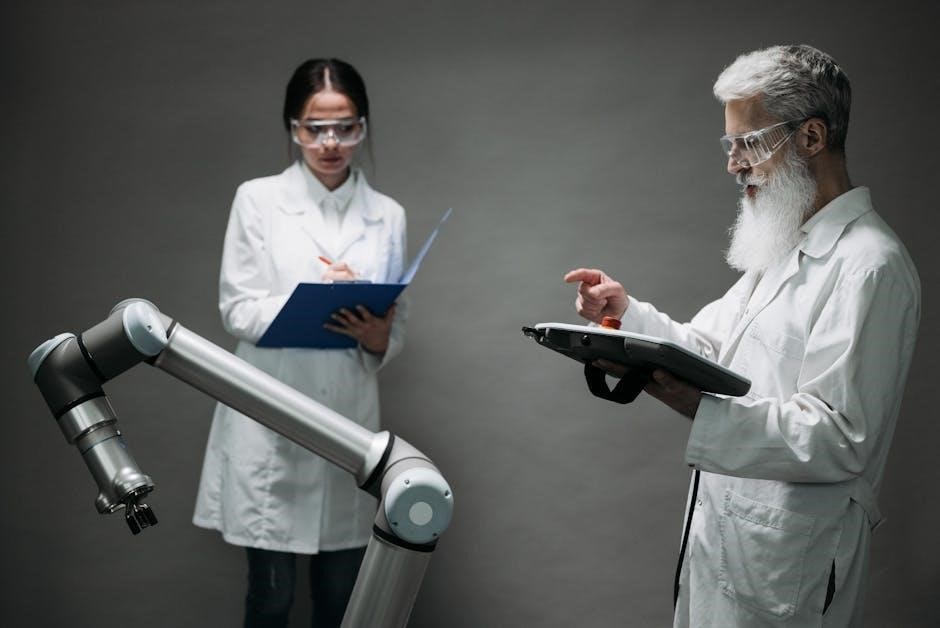

The Chemistry Lab Manual serves as a comprehensive guide for conducting experiments safely and effectively. It outlines essential safety protocols‚ proper handling of chemicals‚ and emergency procedures. The manual emphasizes the development of problem-solving skills through structured experiments and detailed reporting. It provides clear instructions for pre-lab preparations‚ step-by-step procedures‚ and post-lab analyses. This resource is designed to enhance laboratory skills and ensure accurate documentation of experimental data.
Overview of the Lab Manual
The Chemistry Lab Manual is a comprehensive resource designed to guide students through practical experiments and theoretical concepts. It includes detailed sections on safety protocols‚ equipment usage‚ and experimental procedures. The manual covers essential topics such as handling chemicals‚ maintaining laboratory notebooks‚ and understanding MSDS. It also provides step-by-step instructions for experiments‚ pre- and post-lab questions‚ and data analysis techniques. The structure ensures a systematic approach to learning‚ emphasizing precision‚ accuracy‚ and critical thinking. This manual serves as a cornerstone for developing practical skills and fostering scientific inquiry in a structured and safe environment.
Importance of Laboratory Safety
Laboratory safety is paramount to prevent accidents and ensure a secure environment for experimentation. Proper handling of chemicals‚ equipment‚ and hazardous materials is essential to avoid exposure to potential risks. Adhering to safety protocols minimizes the likelihood of injuries‚ spills‚ and environmental contamination. Understanding Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) are critical components of lab safety. Regular training and awareness of emergency procedures‚ such as fire evacuation and chemical spill management‚ further enhance safety. A safe laboratory environment fosters responsible experimentation and protects both individuals and the facility from potential hazards.
Structure and Organization of the Manual
The Chemistry Lab Manual is organized into clear sections‚ each addressing specific aspects of laboratory work. It begins with an introduction‚ followed by safety guidelines‚ equipment details‚ pre-laboratory preparation‚ and experimental procedures. Each section includes pre-lab questions‚ step-by-step instructions‚ and post-lab analyses to guide students. The manual also covers data analysis‚ waste disposal‚ and additional resources like the periodic table. This structured approach ensures a logical flow‚ promoting systematic learning and skill development while emphasizing safety and proper laboratory practices.
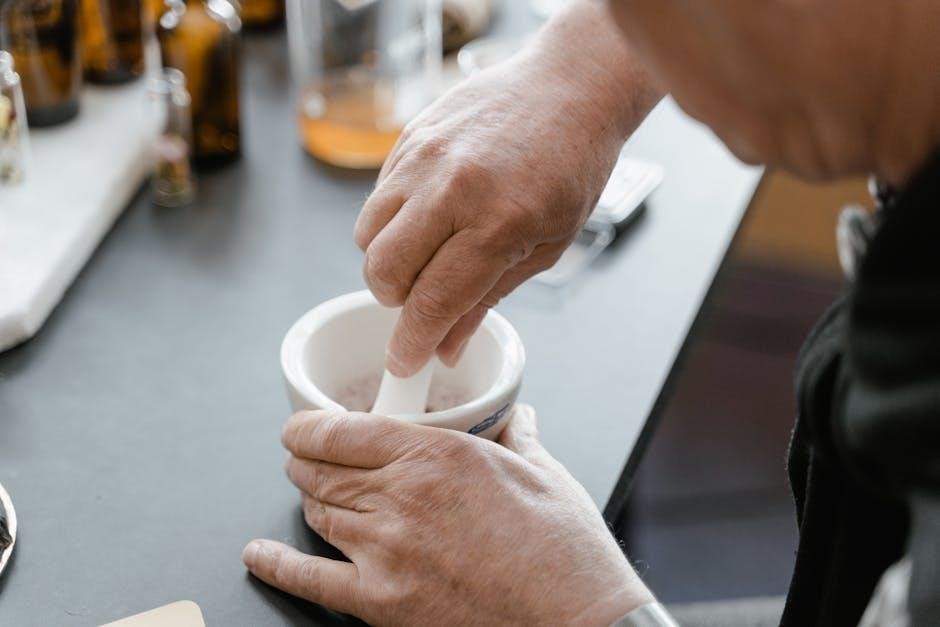

Lab Safety Guidelines
The Chemistry Lab Manual outlines essential safety guidelines to ensure a secure environment. Key areas include general laboratory rules‚ safe chemical handling‚ and emergency preparedness. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is emphasized‚ such as goggles‚ gloves‚ and lab coats‚ to minimize risks during experiments.
General Laboratory Safety Rules
Adhering to general laboratory safety rules is crucial for minimizing risks. Students must wear personal protective equipment (PPE)‚ such as goggles and gloves‚ when handling chemicals. Familiarize yourself with Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for each chemical. Ensure proper ventilation and avoid eating or drinking in the lab. Follow instructions carefully‚ and never mix chemicals without guidance. Keep emergency exits clear and know the location of fire extinguishers and eyewash stations. Dispose of waste correctly‚ and clean up spills immediately. Always maintain a neat workspace to prevent accidents and ensure a safe learning environment.
Handling Chemicals and Hazardous Materials
Proper handling of chemicals and hazardous materials is essential to prevent accidents. Always read labels carefully and use Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for guidance. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE)‚ such as gloves and goggles‚ when handling chemicals. Use tongs or other tools to avoid direct contact with hazardous substances. Store chemicals in their original containers and in designated areas. Dispose of waste according to lab protocols to avoid contamination. Never eat‚ drink‚ or smoke in the lab. Follow specific handling instructions for each chemical to ensure safety and compliance with lab regulations.
Emergency Procedures in the Lab
In case of emergencies‚ act quickly and follow established protocols. For chemical spills‚ contain the area and use absorbent materials. In case of fires‚ use appropriate fire extinguishers and evacuate the lab. If exposed to hazardous chemicals‚ flush with water and seek medical help. For eye exposure‚ rinse with water for at least 15 minutes. Know the location of emergency exits‚ fire extinguishers‚ and eyewash stations. Alert others and contact emergency services if necessary. Always prioritize safety and follow evacuation procedures during critical incidents.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is essential for safeguarding against chemical‚ biological‚ and physical hazards in the lab. Common PPE includes lab coats‚ gloves‚ goggles‚ and masks. Lab coats protect clothing from splashes and spills‚ while gloves prevent skin contact with hazardous substances. Goggles or safety glasses shield eyes from chemical splashes. Masks or respirators are used to filter airborne contaminants. Ensure PPE is properly fitted and worn as required by lab protocols. Regularly inspect PPE for damage and replace it when necessary to maintain effectiveness. Always follow guidelines for PPE use and removal.
Lab Equipment and Instruments
Lab equipment includes microscopes‚ spectrophotometers‚ and centrifuges‚ while instruments like pH meters and thermometers enable precise measurements. These tools are vital for accurate experiments and analysis.
Common Laboratory Equipment and Their Uses
Common lab equipment includes beakers‚ test tubes‚ and Erlenmeyer flasks for holding and mixing chemicals. Bunsen burners provide controlled heat for reactions. Crucible tongs and wire gauze are used for handling hot crucibles. Stirring rods and spatulas assist in mixing and handling solids. Pipettes and burettes measure precise liquid volumes‚ essential for titrations. These tools are fundamental for conducting experiments safely and accurately‚ ensuring precise measurements and efficient chemical handling.
Measurement Tools: Glassware and Instruments
Measurement tools in a chem lab include graduated cylinders‚ volumetric flasks‚ and pipettes for precise liquid measurements. Burettes are used for titrations‚ while measuring pitchers and scoops handle larger quantities. Digital balances and analytical scales measure masses accurately. Spectrophotometers and pH meters are instruments for analyzing concentrations and acidity. These tools are essential for quantitative analysis‚ ensuring accuracy and precision in experiments. Proper calibration and usage are critical for reliable results‚ adhering to laboratory protocols and safety standards.
Electrical and Electronic Devices in the Lab
Lab electrical and electronic devices include Bunsen burners‚ hot plates‚ and stirrers for heating and mixing. Thermometers‚ thermostats‚ and pH meters monitor temperature and acidity. Spectrophotometers and centrifuges are used for advanced analyses. Electrical devices require proper grounding and regular maintenance to ensure safety and functionality. Calibration of electronic instruments is crucial for accurate results. Always follow manufacturer guidelines and safety protocols when operating these devices to prevent accidents and ensure reliable experimental outcomes.
Proper Use and Maintenance of Equipment
Proper use and maintenance of lab equipment ensure accuracy‚ safety‚ and longevity. Always follow manufacturer guidelines and cleaning schedules to prevent contamination and wear. Regularly inspect equipment for damage or malfunction and report issues promptly. Store devices in designated areas to avoid exposure to harmful conditions. Calibration of instruments is essential for reliable results. Train personnel thoroughly on operation and upkeep to maintain functionality and safety standards. Adhering to these practices minimizes errors‚ enhances efficiency‚ and ensures optimal performance in laboratory experiments.

Pre-Laboratory Preparation
Pre-laboratory preparation involves understanding the experiment’s objectives‚ gathering all necessary materials‚ and organizing equipment to ensure efficient and safe execution of procedures and achieve accurate results.
Preparing for Lab Experiments
Preparing for lab experiments involves reviewing the lab manual‚ understanding the procedure‚ and gathering all required materials and equipment. Students should read and familiarize themselves with the experiment’s objectives‚ safety protocols‚ and expected outcomes. Organizing glassware‚ chemicals‚ and instruments beforehand ensures efficiency. Checking equipment for proper function and calibration is essential. Additionally‚ preparing a data sheet or notebook for recording observations and results is recommended. Understanding potential hazards and necessary precautions ensures a safe working environment. Proper preparation minimizes errors and enhances the quality of experimental results.
Writing Pre-Lab Reports and Questions
Writing pre-lab reports and questions is essential for organizing thoughts and understanding experiment objectives. The report typically includes an introduction‚ experiment objectives‚ lists of materials and equipment‚ and step-by-step procedures. Students should also formulate pre-lab questions to guide their investigation and ensure comprehension of key concepts. The report serves as a roadmap‚ helping students stay focused and prepared during the experiment. It also facilitates reflection and analysis‚ enhancing learning outcomes and experimental accuracy. Clear and concise writing ensures effective communication of ideas and procedures.
Understanding Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
A Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) provides critical information about chemical hazards‚ safe handling‚ and emergency procedures. It includes details on chemical identification‚ physical properties‚ health hazards‚ and first aid measures. Sections also cover fire-fighting techniques‚ accidental release steps‚ and proper storage. Understanding MSDS is vital for lab safety‚ helping users assess risks and prevent accidents; It ensures compliance with regulations and promotes safe handling of hazardous substances. Familiarity with MSDS is essential for all lab personnel to maintain a secure working environment and respond effectively in emergencies.
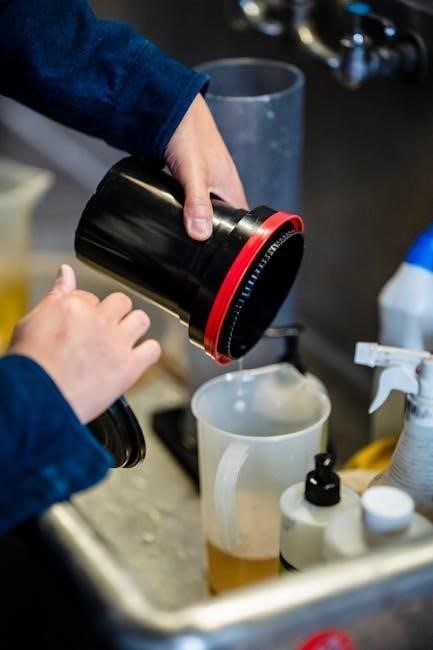

Conducting Laboratory Experiments
Conducting lab experiments requires precise execution of procedures‚ attention to safety protocols‚ and accurate data collection to achieve reliable results and ensure a successful experiment outcome;
Step-by-Step Experimental Procedures
Step-by-step experimental procedures are detailed instructions guiding students through lab experiments. They include the objective‚ materials‚ and sequential actions to ensure clarity and safety. Each step is designed to help students understand the process logically. Proper use of equipment‚ chemical handling‚ and safety protocols are emphasized. Students should follow the instructions carefully to avoid errors and ensure accurate results. These procedures also include calculations‚ observations‚ and expected outcomes to prepare students for the experiment’s execution and analysis.
Recording Observations and Data
Recording observations and data is a critical part of laboratory work. Accurate and detailed records ensure reproducibility and validity of results. Use a lab notebook to document everything observed‚ including measurements‚ colors‚ odors‚ and unusual occurrences. Data should be recorded immediately and objectively‚ avoiding interpretations. Organize information clearly‚ using tables or graphs if needed. Label all data with dates‚ experiment names‚ and page numbers. Consistency and thoroughness are essential for reliable analysis and future reference‚ making it a cornerstone of scientific practice.
Post-Lab Questions and Analysis
Post-lab questions and analysis are essential for evaluating experiment outcomes. Review the objectives to determine if they were met and assess data accuracy. Identify sources of error and their impact on results. Draw conclusions based on observations‚ linking them to theoretical concepts. Reflect on what was learned and how it aligns with predictions. This critical thinking enhances understanding and improves future experimental designs‚ fostering a deeper connection between theory and practical application in chemistry labs.

Post-Laboratory Procedures
Post-laboratory procedures ensure proper cleanup‚ waste disposal‚ and report submission. They promote safety‚ efficiency‚ and accountability‚ adhering to best practices.
Writing Laboratory Reports
Writing laboratory reports is a critical post-laboratory procedure that documents experiment details‚ results‚ and conclusions. A well-structured report includes an introduction‚ materials‚ methods‚ results‚ discussion‚ and conclusion. Clarity and accuracy are essential‚ ensuring data is presented logically. Proper formatting‚ such as using headings and subheadings‚ enhances readability. Including tables‚ graphs‚ and images supports findings. Reports must use appropriate scientific terminology and follow guidelines for significance and precision. They serve as permanent records‚ facilitating future reference and verification of experimental outcomes. Adherence to formatting standards ensures professionalism and accessibility.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data analysis and interpretation are crucial steps in laboratory work‚ transforming raw data into meaningful insights. This involves calculating results‚ identifying patterns‚ and comparing findings with theoretical expectations. Accurate interpretation ensures conclusions are valid and reliable. Graphs‚ tables‚ and statistical tools aid in presenting data clearly. Errors and anomalies are analyzed to assess experimental accuracy. This process enhances understanding of chemical principles and refines experimental methods. Clear interpretation of data is essential for drawing valid conclusions and communicating results effectively in laboratory reports.
Cleaning Up and Disposing Waste
Cleaning up and disposing of waste in a chemistry lab is essential for safety and environmental protection. Proper disposal methods must be followed for both hazardous and non-hazardous materials. Equipment and surfaces should be cleaned and decontaminated thoroughly. Always wear appropriate PPE during cleanup to minimize exposure risks. Chemical waste must be labeled correctly and disposed of according to specific guidelines. Whenever possible‚ consider recycling or neutralizing waste to reduce environmental impact. Maintaining a clean and organized lab environment ensures efficiency‚ reduces contamination risks‚ and prevents potential hazards.

The Role of the Lab Manual
The lab manual serves as a comprehensive guide for conducting experiments safely and effectively. It provides detailed procedures‚ safety protocols‚ and ethical practices for chemical experiments.
Purpose and Scope of the Manual
The chemistry lab manual is designed to guide students through experiments‚ ensuring a safe and educational experience. It outlines procedures‚ safety protocols‚ and expected outcomes‚ helping students master practical skills. The manual covers a wide range of topics‚ from basic to advanced experiments‚ providing detailed instructions and theoretical background. It also includes references to material safety data sheets (MSDS) and ethical considerations. This comprehensive resource aids in understanding chemical principles and fosters critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Designing Experiments and Problem-Solving Skills
Designing experiments is a core skill developed through the chem lab manual‚ emphasizing clear objectives‚ appropriate methods‚ and material selection. Students learn to hypothesize‚ test variables‚ and interpret results. Problem-solving skills are refined as they analyze data‚ identify errors‚ and troubleshoot unexpected outcomes. The manual provides frameworks for experimental design‚ fostering creativity and critical thinking. By addressing challenges‚ students enhance their ability to approach complex scientific questions systematically and effectively‚ preparing them for real-world laboratory scenarios.
Lab Notebook Keeping and Documentation
Lab notebook keeping is essential for documenting experimental procedures‚ observations‚ and results. A well-maintained notebook ensures reproducibility‚ accountability‚ and clarity in scientific work. Entries should be dated‚ detailed‚ and include raw data‚ calculations‚ and conclusions. Proper documentation also facilitates peer review and serves as a legal record for intellectual property. The chem lab manual emphasizes organization‚ neatness‚ and accuracy‚ teaching students to standardize entries and maintain a comprehensive record of their laboratory activities for future reference and professional development.

Quantitative Analysis in the Lab
Quantitative analysis involves measuring chemical quantities to determine concentrations‚ masses‚ or volumes. It ensures accuracy and precision in experimental results‚ crucial for reliable data interpretation.
Quantitative methods in chemistry involve precise measurements and calculations to determine concentrations‚ masses‚ or volumes. These techniques are essential for accurate experimental outcomes.
Common methods include spectrophotometry‚ chromatography‚ and titration‚ which provide numerical data for analyzing chemical reactions and stoichiometry.
Calibration and standardization are critical to ensure instrument accuracy and reliable results‚ enabling chemists to draw precise conclusions and understand chemical processes effectively.
Titration and Chromatography Techniques
Titration is a precise method for determining the concentration of a solution by reacting it with a standard solution of known concentration. Acid-base and redox titrations are common‚ relying on color changes or electrodes for endpoint detection.
Chromatography separates and identifies components in a mixture. Techniques like paper‚ thin-layer‚ and gas chromatography are used to analyze substances based on their movement through a stationary phase.
- Titration ensures accurate concentration measurements.
- Chromatography aids in separating and identifying compounds.
Error Analysis and Significant Figures
Error analysis evaluates uncertainties in measurements‚ crucial for assessing experimental accuracy. Random errors are minimized through repeated trials‚ while systematic errors require calibration or method adjustment.
Significant figures ensure precision in recorded data‚ reflecting the reliability of measurements. Proper handling maintains data integrity throughout calculations and reporting.
- Error analysis identifies and reduces measurement uncertainties.
- Significant figures prevent overrepresentation of precision.
- Both are essential for valid and reproducible results.

Additional Resources
The manual includes a periodic table‚ supplementary guides‚ and online resources for further learning and reference‚ enhancing experimental understanding and technical skills in chemistry labs.
Periodic Table and Chemical References
The manual includes a detailed periodic table‚ listing elements with their symbols‚ atomic numbers‚ and weights. It also provides chemical references‚ such as molecular formulas‚ molar masses‚ and solubility rules. These resources aid in identifying elements and compounds‚ predicting chemical behavior‚ and understanding reactions. Color-coded groups in the periodic table highlight metal‚ non-metal‚ and noble gas categories. Additionally‚ chemical references offer safety data and handling guidelines‚ ensuring accurate experiment planning and execution. These tools are essential for students and researchers to interpret and apply chemical information effectively.

Supplementary Materials and Guides
The manual includes supplementary materials such as diagrams‚ charts‚ and quick reference sheets to aid in complex procedures. Additional guides provide step-by-step instructions for specialized techniques‚ troubleshooting common issues‚ and optimizing experimental outcomes. These resources complement the main content‚ offering practical tips and best practices. They are designed to enhance understanding and proficiency‚ ensuring students and researchers can confidently navigate challenging lab scenarios. The supplementary materials are organized for easy access‚ making them invaluable for both beginners and experienced laboratory practitioners.
Online Resources for Lab Manual Support
The lab manual is supported by online resources‚ including interactive tutorials‚ video demonstrations‚ and downloadable worksheets. These resources provide additional explanations for complex procedures and offer troubleshooting tips. Online forums and discussion groups allow users to share experiences and solutions. Webinars and virtual labs enhance hands-on learning‚ while updated databases ensure access to the latest chemical information. These digital tools complement the manual‚ fostering a deeper understanding and improving experimental outcomes for students and researchers alike‚ making them an essential companion to the lab manual.




